Medical
Medical Wastewater Treatment
HHospital sewage, especially in infectious disease hospitals and tuberculosis hospitals, contains a variety of bacteria, viruses, parasitic worm eggs and some toxic and harmful substances in varying degrees. These germs, viruses and parasitic worm eggs have a certain resistance in the environment, and some survive in sewage for a long time. When people eat or contact the water or vegetables contaminated by bacteria, viruses, parasitic worm eggs and toxic and harmful substances, they will make people sick or cause the outbreak of infectious diseases. In recent years, cholera has occurred in many countries of the world, with unprecedented outbreaks and deaths, mostly in the coastal areas of underdeveloped countries, and has reportedly been caused by contaminated drinking water with the excreta of patients.

The main reason why bacteria, viruses or parasitic eggs can be transmitted by water is that the content of pathogens in sewage is large. Another reason is that pathogens have strong resistance to environmental physical and chemical factors, and their survival rate is relatively high in the environment. For example, e. coli can survive in river water for 21-183 days, s. dysenteriae can survive in river water for 12-92 days, and Vibrio cholerae can survive in river water for 0.5-92 days. The virus is more resistant to environmental factors, with hepatitis virus surviving for 70 days in sewage, poliomyelitis for 3-4 months and leptospirals surviving for 30 days. Sars-cov can survive in sewage for only 3-4 days. Although THE environmental tolerance of SARS-coV is not stronger than that of hepatitis virus and dysentery bacillus, it has been mentally troubled by its rapid onset, rapid transmission, high mortality rate, and lack of source, transmission, corresponding methods and treatment methods.

Primary treatment process
The main purpose of the conventional primary treatment is to remove floating and suspended solids (SS) in the sewage to create conditions for subsequent treatment. Its main equipment and structures are: grille, sedimentation tank, sedimentation tank, etc. The grille removes large particles and floating solids from the sewage. The sedimentation tank can remove more than 0.2mm of sand, and the sedimentation tank can remove most of the suspended solids in sewage. Generally, 60% suspended solids and 20% BOD5 can be removed by primary treatment.
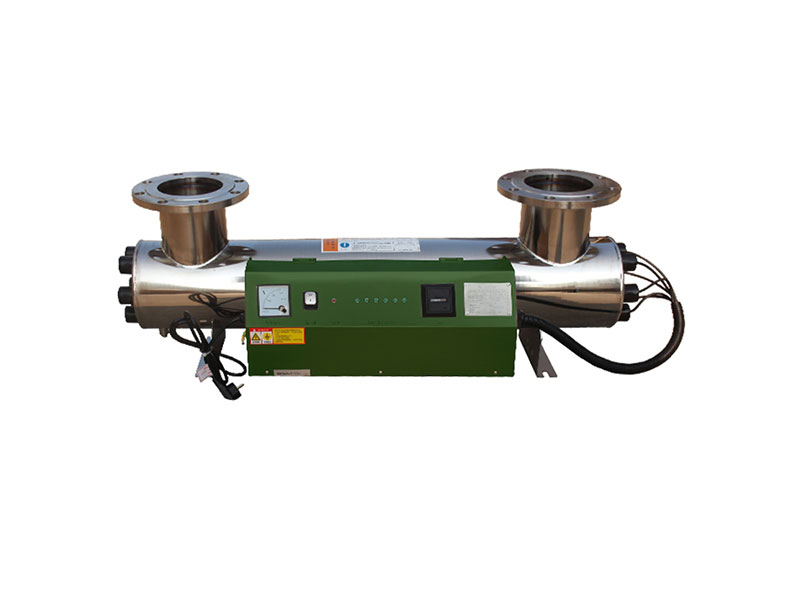
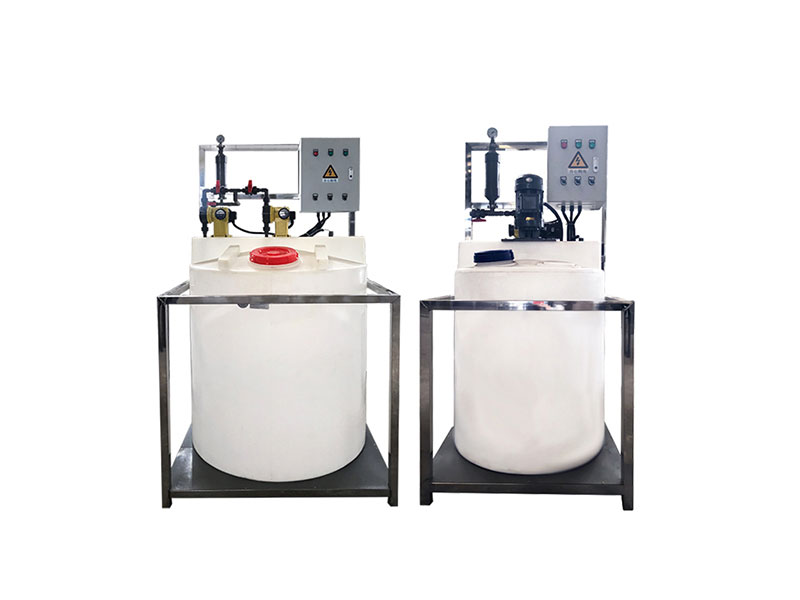
The typical process of primary treatment and chlorination disinfection of hospital sewage is: the sewage from ward and other bacteria-containing sewage is collected to the sewage treatment station through the drainage pipe, and the fecal sewage should first be precipitated and digested by the septic tank, and then enter the sewage treatment station. The processing station is equipped with grille, regulating pool, metering pool, lifting pump and contact pool. After interworking with water pumps or mixing with siphon water, the disinfectant enters the contact pool. After the sewage and disinfectant in the contact pool meet the requirements of water purification and disinfection for a certain period of time, it is discharged. The settled sludge produced by septic tank or sedimentation tank is regularly eliminated and disinfected according to the regulations. The typical process can be simply shown in Figure 2.1
Secondary treatment process
Secondary treatment mainly refers to biological treatment. Biological treatment can remove dissolved and colloidal organic pollutants from sewage. The removal rate of BOD is more than 90%, and the BOD of effluent can be reduced to less than 30mg/L. At the same time, organic pollutants such as COD, phenol and cyanide can also be removed. Conventional secondary biological treatment techniques such as activated sludge cannot remove nitrogen and phosphorus from water. Therefore, an improved secondary treatment technology for biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal has been developed at home and abroad. It is often used in combination with secondary treatment, and sometimes is to transform the conventional biological treatment facilities, so that it has the function of nitrogen and phosphorus removal. The technologies used are A/O method, A/O method, SBR method, AB method, oxidation ditch and biofilm method.
Traditional activated sludge process
Conventional activated sludge system with rectangular profile type aerator, first enter the backflow of sewage and sludge from the pool, and mixture with piston stream flow gradually to pool tail flow, from the end of the pool water weir flow, into the second pond, in the mud in the pond to complete separation of post-processing water discharge, precipitation sludge circumfluence to the aeration tank, into the next cycle.
Adsorption regeneration
The main feature of this mode of operation is that the two processes of degradation of organic matter by activated sludge, initial adsorption and biological metabolism, take place in two structures or two stages of a structure, respectively.
Medical sewage treatment SBR method
SBR process is a batch activated sludge system, also known as sequence batch activated sludge system. The aeration tank of SBR process is completely mixed in the flow mode, but in the degradation of organic matter, it is the push of time. Organic matter is degraded over time, and its basic operation process is composed of five basic processes, such as inlet, reaction, precipitation, effluent and idle. A cycle is formed from sewage to idle end. In each cycle the above processes are carried out sequentially in a reactor equipped with aeration or agitation.
AB method
AB method is biosorption degradation method. Grade A operates with high or super high load (sludge load >2.0kgBOD5/kgMLSS· D), and Grade B operates with low load (sludge load is generally 0.1 ~ 0.3kgBOD5/kgMLSS· D). A and B have independent sludge return system, and the sludge of the two stages does not mix with each other. The process is stable and has the ability to resist impact load and PH value change. The process can also be built in stages according to economic strength. If A class can be built first, in order to reduce A large number of organic matter in sewage, to achieve better than the first treatment effect, such as conditions mature, then build B class to meet higher treatment requirements.
A/O and A2/O methods A/O systems and A2/O systems are composed of anoxic-aerobic or anoxic-anoxic-aerobic systems
Biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal process of wastewater consisting of biological treatment.
CASS process biochemical treatment
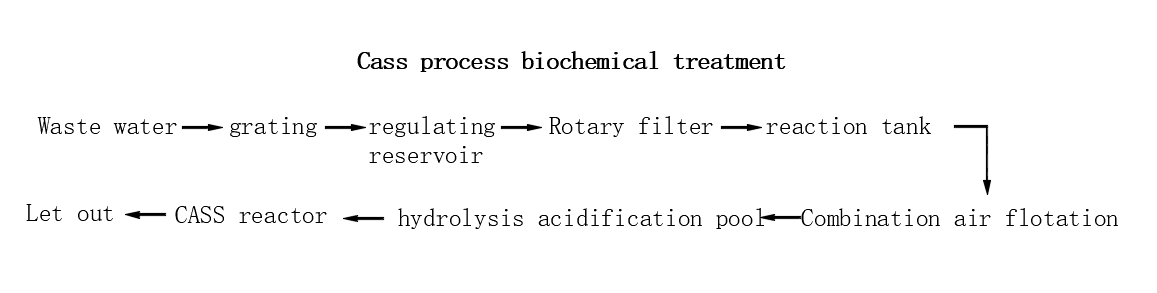
The main reaction of CASS process is to distinguish anoxic and aerobic parts, and aeration, precipitation and skimming are carried out periodically. Due to periodic aeration, the oxygen concentration gradient is large, the transfer efficiency is high, the energy saving effect is obvious, and the operation cost can be reduced by about 20%.
Biodegradation, sludge sedimentation and wastewater discharge of CASS process are all carried out in the same tank, without regulating tank, secondary sedimentation tank and sludge reflux equipment, which can greatly save investment, reduce operating costs and reduce land use. The CASS process adopts delayed aeration, which makes the sludge yield low and water dewatering good. The application of new underwater aeration equipment and special floating skimming device which can automatically lift makes the system simple, flexible and stable.
CASS method mainly adopts anaerobic and oxygen-combined biological treatment, and with a series of physical and chemical means to precipitate, decompose and kill the organic matter, bacteria and viruses in sewage. At the same time, it also has a good function of removing nitrogen and phosphorus, so that the investment of secondary treatment can reach the effect of tertiary treatment of effluent quality.
Each CASS reactor consists of three parts: biological selection zone, anoxic zone and aerobic zone. The volume ratio of the three zones is about 1:2:27. The biological selection zone is actually a small volume of sewage and sludge contact zone. By aerobic zone backflow activated sludge and biological selection area mixed with fresh water, touch, and create the microbial population competition under high load condition, select out the advantage of effectively inhibiting filamentous bacteria breeding, improve the system stability, rapid adsorption of activated sludge at the same time to speed up the solubility of substrate removal, the hydrolysis of the refractory organic matter and play a good role, still can make Phosphorus in sludge can be effectively released under anaerobic conditions.

The anoxic extraction area can assist the biological selection area to buffer the change of water quality and quantity. In this area, the organic matter is mainly removed by the adsorption of regenerated activated sludge, and the removal rate is more than 80%. Meanwhile, it can promote the further release of phosphorus and strengthen the denitrification. Aerobic zone is the main place where microorganisms decompose the adsorbed organic matter. Its operation cycle includes four stages: water filling, aeration, water filling, precipitation, night clearing and water filling, and idling. Different operation stages and time can be adjusted according to the quality of the treated sewage. The operation cycle is repeated, and the effective volume of sewage in the reaction is a variable value. In this method, the sequential batch operation is as follows: anaerobic → anoxic → aerobic → anoxic → anaerobic.